SEO is in a state of rapid change. The core components of SEO in 2025 will be the people, places, concepts, and things that give search results context and meaning, which is why semantic SEO is now considered in modern engines like Google and others that index and rank SEO entities. In the past, search engine algorithms matched strings of keywords to user queries.
Today, knowledge graph SEO, AI ranking, and neural search models are driving modern search results. Building authority in the modern era means knowing how entities connect, not just how keywords rank.
In this guide, we’ll discuss what SEO entities are, why entities matter for modern SEO, and how businesses can use entity-based SEO to establish authority and trust for their brand.
What are SEO Entities?
An SEO entity is any unique recognizable item, such as a person, location, company, idea, product, or brand. SEO entities are not just words, they are unique “nodes” in Google’s knowledge graph.
For example:
- “Barack Obama” → an entity (person)
- “iPhone 15” → an entity (product)
- “Climate change” → an entity (concept)
If you’re just starting to get the concept of SEO entities, a detailed entity SEO guide will ensure that you can move from keyword-driven SEO to entity-centric SEO with confidence.
Keywords vs. Entities
Old-school SEO meant exact-match keyword optimization, such as “best pizza New York.” Entities take it a step further. Rather than just indexing those words, Google can understand “pizza” as a food entity and “New York City” as a location entity. That allows Google to relate connections, such as “style,” “restaurants” and “map” to more than just the exact phrase.
Search results have already changed in this direction. Look at featured snippets, knowledge panels, or AI overviews. They all rank entities instead of trying to match keywords.
Why Entities Matter for SEO in 2025
Semantic Search and AI Overviews
AI is reshaping the SEO landscape. Search engines like Google and Bing now process queries using semantic SEO methods, meaning they focus more on understanding the meaning behind searches, rather than simply string matches. Entities allow Google to disambiguate terms in queries and provide context. For example, “apple” is a word with two different meanings, it can be a fruit or tech company. Entity recognition helps make sure people see the right results.
E-E-A-T and Entities
Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) is connected to entities. When Google can easily identify a business or brand as an entity, it gives Google more confidence in your site as a source of authority on related topics. This, in turn, helps to build topical authority and qualify your brand for visibility in AI-generated search overviews.
Long-Term Authority
Entity-based optimization is the key to long-term value, as it prioritizes intent and relevance over keyword density. For example, “keyword stuffing” by itself will not future-proof your SEO by 2025. Entities matter because they:
- Improve contextual relevance
- Support Google’s Knowledge Graph
- Increase exposure in conversational search

How Google Identifies and Connects Entities
The Knowledge Graph
Google’s Knowledge Graph was first launched in 2012. It’s a vast web of related concepts and entities, with known relationships mapped between them. The Knowledge Graph powers:
- Related searches
- Featured results
- Knowledge panels on the right sidebar
When you search for “Marie Curie”, Google is not pulling just those terms; it’s pulling a pre-established entity, with various “attributes” that make up the whole person, like “scientist,” “Nobel Prize,” and “radioactivity.”
Google SEO entities are the basic units of the Knowledge Graph, which allow the search engine to relate queries with significance on a deeper level.
Entity Relationships
Google also determines how entities relate by analyzing which ones commonly co-occur in real-world data (content). For instance, the entity “yoga” is associated with the entities “flexibility,” “wellness,” and “meditation.” Publishing information about the entities associated with your topic tells Google you’re relevant. Google’s understanding of entities is constantly growing through AI and machine learning, so it can make connections even if they aren’t stated directly in the text.
Structured Data & Schema
Schema markup tells search engines explicitly what your content is about. By adding markup related to entities on your web page, you give Google hints about the entity your site is about, whether that’s a brand, product, event, or person.
Structured data is a fundamental building block of entity SEO.
Building an Entity-Based SEO Strategy
Step 1: Entity-Based Keyword Research
SEO marketers often want to know how to find SEO entities. The secret is to correlate your keyword data with semantic tools that will show you related people, places, and concepts. That means, you don’t have to obsess solely about search volume keywords.
Instead, the use of tools such as Google’s NLP API and InLinks are regarded as the best way to find SEO entities which fit your business niche and are being ranked for by your competitors. This is the best approach to discovering new SEO entities related to your business.
To learn more on strengthening your technical SEO foundation, which is especially important when shifting focus from keywords to entities, check out WiRe Innovation’s detailed guide on fixing common SEO errors.
Step 2: Map Relationships
Create an entity relationship mapping diagram. Visually map out how the core entities for your niche relate to one another. For example, if your niche is fitness, you might start with a central entity like this:
Central entity → “Strength training”
Related entities → “weights,” “hypertrophy,” “protein intake,” and “muscle recovery”
Step 3: Content Clusters
Use content cluster optimization to reinforce topical authority. Content clustering strategies build entity authority through networks of interlinked articles that build support for a pillar topic. The pillar page describes the primary topic or entity, then cluster content is built that goes in-depth with related sub-entities.

Optimizing Content for Entity Salience
Entity salience describes how prominently an entity is presented in content. Optimizing entity salience in content involves ensuring that your most important concepts are clearly highlighted via headings, links, and context.
To optimize entity salience:
- Use headings strategically: Make sure key entities are used in H2s and H3s to give Google search engines search context.
- Leverage internal linking: Link between related entity pages and use anchor text to show relationships and signal authority.
- Embed context naturally: Don’t keyword-stuff. Instead, use synonyms, related concepts, and real-world examples.
- Balance readability and optimization: Content should always prioritize readability for the reader first and foremost. Entities should feel natural in context.
Leveraging Structured Data for Entity SEO
Structured data for SEO works as a translator. It tells search engines which entity the page is and how it should be classified.
Schema Types That Define Entities
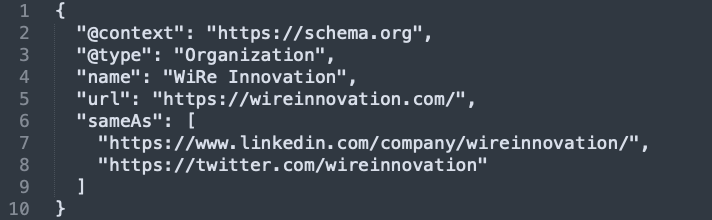
- Organization schema: This is where you define your business organization.
- Person schema: Helps to define author experience. Useful for E-E-A-T.
- Product schema: Use this to make your products more visible in search results.
- Event schema: Help your event entities find the right place and time.
Example
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Schema markup that doesn’t clearly align to the real attributes of an entity.
- Generic schema markup that doesn’t connect your entity to the Knowledge Graph.
- Forgetting to validate your schema markup with a tool like Schema Markup Validator.
Measuring Success With Entity SEO
Key Tracking Methods
- Google NLP API: See how Google’s Natural Language Processing tool surfaces entities in your content.
- Knowledge panel monitoring: Track whether your brand or topic entity begins to appear in the right-hand search results.
- Entity SEO tools: Use SEO platforms like InLinks, MarketMuse, or WordLift to track entity salience and relationship mapping.
- Topical authority shifts: Monitor to see if your brand improves performance in semantic search optimization and is included in AI overviews.
How SEO Entities Fit Into a Full SEO Strategy
SEO entities are not the opposite of keywords, they’re just an evolution. Successful SEO strategies in 2025 will not rely exclusively on entities. Instead, the smartest brands weave both together.
- Entity + keyword research: Discover related search demand and context.
- Schema markup for entities: Adds strong data points to help Google connect your brand to known entities.
- Content clusters: Ties entities together in a web of topical authority.
- Entity salience optimization: Ensures clarity for both human and machine readability.
If you are transitioning from traditional keyword SEO to entity-based search, start with WiRe Innovation’s semantic SEO guide and SEO vs. AEO breakdown. Both guides break down how to shift your SEO strategy to optimize for 2025’s AI-driven landscape.
Conclusion
The future of SEO is all about relationships. Keywords still matter but the real power is in the nodes of connection, like the people, places, concepts, and things that make up SEO entities. By focusing on the things Google evaluates (structured data, content clusters, entity mapping), brands can build topical authority, strengthen E-E-A-T signals, and win a spot in AI-powered search results.
In 2025, the most competitive brands will be those who embrace an entity-first approach to SEO. The best place to start is to consider your brand, your expertise, and your content as SEO entities that Google should recognize, connect to other entities, and reward.
If you’re ready to upgrade your SEO, contact WiRe Innovation to build your SEO entities-based SEO strategy.



